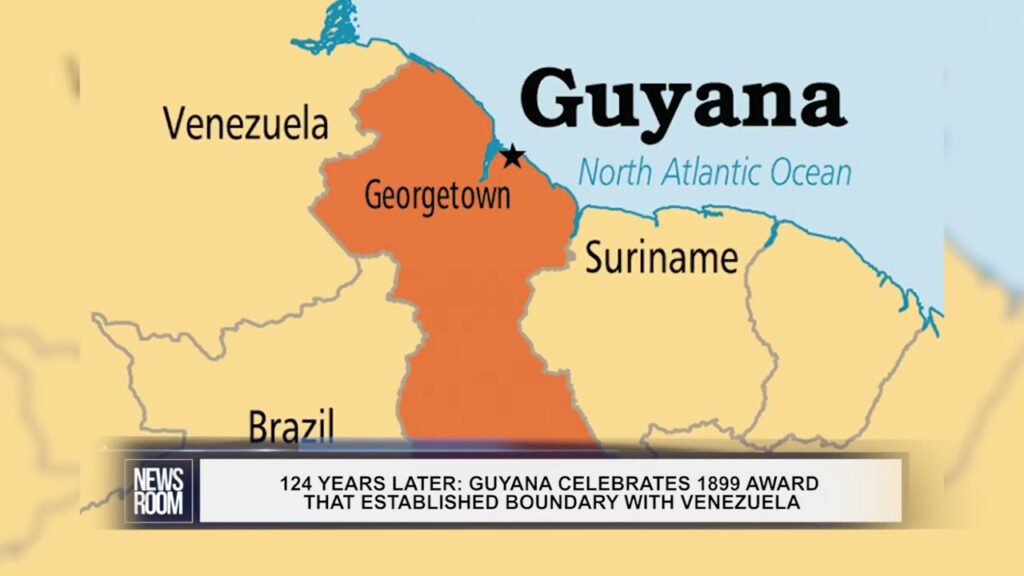
Two South American nations, Guyana and Venezuela, have been entangled in a longstanding border dispute over the Guayana Esequiba region, a crucial area encompassing nearly two-thirds of Guyana’s territory and home to 125,000 of its citizens. This disagreement traces back to historical claims, colonial legacies, and resource discoveries, notably the oil reserves found in the Essequibo region in 2015.
Understanding the Historical Roots
Colonial Legacy: Seeds of Conflict
The conflict dates back to colonial times when Spain controlled Venezuela and the Netherlands and the United Kingdom held sway over Guyana. The foundation of the dispute emerged in 1841 when Venezuela contested British encroachment on its territory, fueling tensions that persisted even after Guyana gained independence from the UK in 1966.
The conflict started when Venezuela objected to the Schomburg Line in 1841.An English expedition delineated the boundaries of Guyana, which it had acquired from the Netherlands.Britain gained command over the Orinoco River’s mouth thanks to the line.Venezuela declared that the United Kingdom was invading its land.
The Essequibo region of Guyana, which makes up about two thirds of the country’s land, is the subject of dispute.An international tribunal established the Essequibo region’s borders in 1899.
The Arbitral Award of 1899: Source of Discord
The core bone of contention lies in the Arbitral Award of 1899, which established the boundaries of the Essequibo region. Venezuela staunchly denounces this award, labeling it an “Anglo-Russian conspiracy,” while Guyana asserts that the award definitively clarified the boundary between the two nations.
Escalation Over Resource Discovery
Oil Reserves and Intensified Conflict
The situation escalated dramatically in 2015 when substantial oil reserves were discovered just off the Essequibo region’s coast. This discovery triggered a surge in the dispute’s intensity, with Venezuelans endorsing a claim to sovereignty over the region through a referendum.
2018: A Step Toward Resolution?
Seeking a resolution, Guyana approached the International Court of Justice (ICJ) in 2018 to settle the conflict. However, despite this effort, a conclusive decision remains distant, with the process potentially taking several more years.
The Contentious Points of Argument
Historical Claims: Spain’s Influence
Venezuela’s contention revolves around the fact that both Essequibo and Venezuela were under Spanish administration during the colonial era. This historical association forms the bedrock of Venezuela’s claim to the Essequibo region.
Disputed Legitimacy: The 1899 Ruling
The international community has recognized the Essequibo region as part of British Guiana (now Guyana) for over a century following the 1899 arbitration. However, Venezuela steadfastly rebuffed the decision, alleging fraudulence.
What Lies Ahead?
The Lengthy Quest for Resolution
Guyana’s pursuit of ICJ intervention offers hope for a definitive resolution. However, the prolonged legal proceedings mean that a conclusive decision remains a distant prospect, leaving both nations in a continued state of dispute.
International Implications
The ongoing dispute has far-reaching implications, not only for the two countries involved but also for regional stability and diplomatic relationships among neighboring nations in South America.
Conclusion
The border dispute between Guyana and Venezuela is a complex and deeply rooted issue, influenced by historical events, colonial legacies, and recent resource discoveries. Despite efforts to seek resolution through international intervention, a definitive solution to this protracted disagreement remains elusive.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
1. What sparked the border dispute between Guyana and Venezuela?
The dispute originated from historical claims dating back to colonial rule, exacerbated by the Arbitral Award of 1899 and intensified with the discovery of oil reserves in the Essequibo region in 2015.
2. Why does Venezuela reject the 1899 Arbitral Award?
Venezuela contends that the award was part of an alleged Anglo-Russian conspiracy and disputes its legitimacy, claiming the Essequibo region as its own territory.
3. What steps has Guyana taken to resolve the conflict?
In 2018, Guyana sought intervention from the International Court of Justice (ICJ) to settle the dispute, aiming for a definitive resolution through legal means.
4. What are the implications of this dispute beyond Guyana and Venezuela?
The dispute’s ramifications extend beyond the two nations, impacting regional stability and diplomatic relations among neighboring countries in South America.
5. When can we expect a resolution to the ongoing conflict?
Given the complexities and legal procedures involved, a conclusive resolution through the ICJ or other means might take several more years, leaving the situation in a state of prolonged dispute.